Solar energy generation is a hot topic globally today because it carries the potential of lowering carbon emissions especially in a world expecting huge climate change repercussions. Besides that, it is a renewable and clean energy source that can be cost effective to maintain once the system has been initially installed.

Image Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/chriskantos/2351716097
Solar Panels can supply reliable power to homes in places of unstable grids or in rural areas where there are no power grids. Advances in photovoltaic technologies and lowered costs continue to make solar power more affordable to home owners. In this article we discuss in details all aspects of solar energy for home use, such as cost to install, requirements, tax benefits etc.
We hope you will find our guide useful.
Here are the topics we will be talking about:
How Do Solar Panels for Homes Work
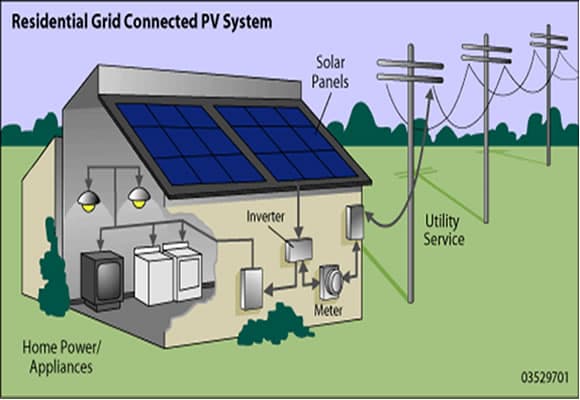
Image Source: https://pureenergies.com/us/how-solar-works/how-solar-panels-work/
Solar energy works by means of a solar panel converting sun energy into clean electrical power that can then be used to power your home devices. You basically need photovoltaic panels that convert sun light into Direct Current (DC current) and then an Inverter device that converts Direct Current into Alternating Current (AC current) which is used by all home appliances.
Other components of a solar panel system include a utility meter to measure your usage and for monitoring the system to ensure the whole set up is working optimally and to signal for repairs when needed.
As shown from the figure above, your residential Photovoltaic (PV) System can be also connected to the electricity utility Power Grid so that you can either send excess electricity back to the power grid (and earn money) or receive electricity from the Power Grid in case the solar system does not generate enough energy for your home.
Most jurisdictions allow for solar credits where individuals generating solar power can share the unused power into the national grid and earn credits. These credits are used to offset the cost of electricity for the home owner.
Have a look at the excellent video below which describes in simple words how solar systems for homes work:
Advantages and Disadvantages of Solar Energy for Home Use
After we’ve got an idea of how solar panels for homes work, let’s now see the advantages and disadvantages of this form of alternative energy for home use. The lists below do not cover all the pros and cons, but the main ones are included.
Advantages of Using Solar Panels on your Home
- The first and biggest advantage for home owners is money savings on Electricity bills. Although there is an upfront cost of purchasing and installing the Photovoltaic System (PV) on your home, I would say this cost should be considered an “investment” since you will have almost zero cost on your electricity bill for the next 20+ years (more discussion on cost and money savings later in this article).
- Solar power provides energy independence. Once you have the solar panels installed (on your roof most probably), then you have an independence from the power grid. What if there is power outage or a disaster strikes the power plant in your area? You will still have electricity from the solar system.
- Very low maintenance required compared to other green energy sources. Solar panels are “passive”, meaning they produce electricity without having any mechanical or moving parts (like wind generators for example).
- Solar panels are totally noise-free.
- No interference to residential lifestyle since they are installed on rooftops most of the times without much trouble.
- No pollution. Solar energy is probably the cleanest renewable energy on earth.
- Relatively reliable energy production. As long as there is light outside, the panels will continue to produce electricity.
- Increase in your home value. A solar panel system will increase the value of your house by around $20,000 [1]
Disadvantages of Using Solar Panels on your Home
- Money is the biggest advantage but can also be the biggest disadvantage for some people. There is an initial investment needed to purchase and install the solar panels system (more on cost etc later on).
- Another disadvantage is that the solar panels do not produce electricity during the night, so you will need another source of power (or maybe use batteries to provide energy for the night which however will increase the initial cost of the system). This is not actually a problem since almost all Solar Systems are connected also to the normal power grid so you will continue to have electricity supply during the night.
How much do solar panels cost
This is the most important question for most people looking to utilize solar energy for home use. The initial cost of purchasing and installing a Photovoltaic System is crucial for many home owners and will dictate whether the use of such a system is worth it or not. Fortunately, as we will see below, this cost will not break the bank for most people and you will get your money back in a few years in most cases.
The cost of a solar panel system (including of course all of the components of the system such as inverter, panels, meter, labor cost etc) vary a lot and depends on a number of factors such as the size of the installation, the state you live in, whether there are tax or other incentives etc.
To get a rough idea, the cost range of solar panels is within $10,000 to $50,000. However, in most cases, the cost is somewhere in between the above range.
Average Solar Panel Cost per Watt Calculation
Usually, the cost of a solar system is calculated per Watt power needed for each home.
Average Cost Case Study:
Let’s see an average calculation of solar panel cost below:
The “average” house in the US requires around 900KWh/month (900 thousand kilowatt-hours).
If you leave in a state where there is average sun light of around 5 peak hours/day, this means you need a solar system of around 7.5kW.
The average cost per Watt for a full installation is around $4/watt (including installation costs + system cost).
Therefore to install a 7.5kW system you will need around $30,000.
Deducting the Federal Tax Credit of 30% ($9,000), the final Net Installation Cost is $21,000.
In the link below you will find an excellent calculator and description how to estimate the cost of a solar panel system for your home:
http://michaelbluejay.com/electricity/solar.html
How Big Should my Solar System be (in kW) ?
Now let’s calculate how to size your system in kW (kilo watts).
Assuming, you want to install a system which will supply 100% of your electricity requirements.
Step1:
Find your daily usage in kwh/day (kilowatt hours per day). This can be found from your electric bill or by calling your utility company.
Average homes in the USA require 900 kwh/month which is around 30kwh/day.
Step2:
Find out the average peak sun hours per day that you get in your area.
From the map below, states in Green have around 3-4 peak sun hours/day, states in Yellow have around 5-6 peak sun hours / day and states in Orange have around 6-7 peak sun hours/day.
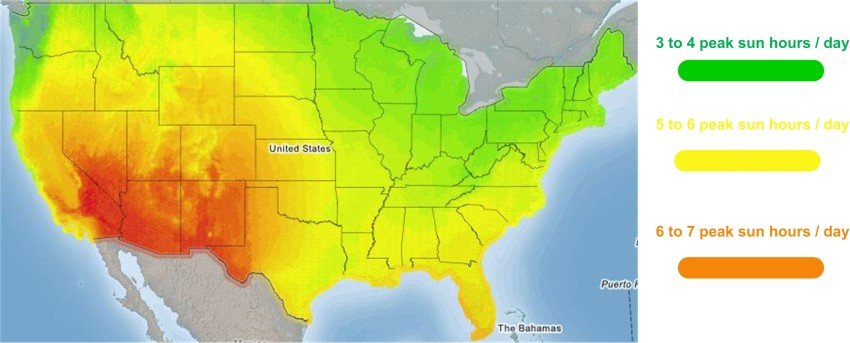
For our case study here, let’s assume that we have 5 peak sun hours/day.
Since you need to generate 30kwh/day (from Step1 above), your solar system should be:
30 kwh / 5 hours = 6kw
Step 3:
Add a safety margin to balance for problems like dust, shading, extended days with low light etc.
6kw x 1.25 [2] safety margin = 7.5 kw solar system (to supply 100% of your electricity needs).
Note: Have a look also at this online government calculator (PVWatts [3] ) to estimate and size your system’s capacity depending on your location.
Types of solar panels
There are mainly three types of solar panels used in homes:
- Monocrystalline
- Polycrystalline
- Thin film
Monocrystalline solar panels:
These are made from silicon wafers produced by cutting four sides out of the cylindrical silicon ingots. They have the highest grade silicon and thus offer the highest efficiency of around 15-20% (higher efficiency means that they produce more electricity with the same amount of light compared to other panels). They are also space efficient and for the same space, they produce four times more power than the thin-film solar panels. They have also higher life-expectancy (usually 25+ years) but they are also the most expensive. They are recognized by their even coloring and uniform look.
Polycrystalline silicon solar panels:
Polycrystalline panels are less efficient than Mono and offer around 13-16% efficiency. They are produced by melting raw silicon and pouring it into a square mold. The mold is cooled and cut into cylindrical wafers. They are not only simpler and less costly to make than the monocrystalline types, but also less material is wasted during the making process. The panels appear bluish in color and look perfectly rectangular with no rounded edges.
Thin film solar panels:
These are the least expensive but also the least efficient (with an efficiency rating of around 7–13%). They are manufactured by depositing a photovoltaic cell onto a substrate and are characterized based on the photovoltaic material in question. They are cheaper to make than silicon based models (monocrystalline and polycrystalline) since it is easy to mass produce them. Although they are cheaper, they require lots of space, and are not generally suited for residential homes. Their life span is also less than the other two types mentioned above.
Solar Tax Credits
The US government decided in December 2015 to extend the 30% Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) until the end of the decade[4]. The Tax credit will continue to exist until 2022 with gradually reduced tax credit levels as shown below:
Solar-electric property:
- 30% for systems placed in service by 12/31/2019
- 26% for systems placed in service after 12/31/2019 and before 01/01/2021
- 22% for systems placed in service after 12/31/2020 and before 01/01/2022
- There is no maximum credit for systems placed in service after 2008.
- Systems must be placed in service on or after January 1, 2006, and on or before December 31, 2021.
- The home served by the system does not have to be the taxpayer’s principal residence.
“A taxpayer may claim a credit of 30% of qualified expenditures for a system that serves a dwelling unit located in the United States that is owned and used as a residence by the taxpayer. Expenditures with respect to the equipment are treated as made when the installation is completed. If the installation is at a new home, the “placed in service” date is the date of occupancy by the homeowner. Expenditures include labor costs for on-site preparation, assembly or original system installation, and for piping or wiring to interconnect a system to the home. If the federal tax credit exceeds tax liability, the excess amount may be carried forward to the succeeding taxable year. The maximum allowable credit, equipment requirements and other details vary by technology, as outlined below.”
Source: http://energy.gov/savings/residential-renewable-energy-tax-credit
What is Solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC)
The solar Investment Tax Credit (ITC) is applicable to both commercial and residential properties. Based on the amount of investment made on a solar system, the ITC tax credit is dollar-for-dollar reduction in the individual’s income tax that would otherwise have been paid to the federal government. The amount is 30% of the initial cost of the solar system as described above. For example, if you install a $30,000 solar system, you will lower your income tax bill by $9,000.
The success of Solar Tax Credit (or the solar Investment Tax Credit – ITC) cannot be gainsaid, having helped the United States incur unprecedented growth in solar energy installations and solar power generation. It has helped to realize a growth of annual solar installation capacity by 1600 percent since introduction in 2005. Particularly, it helped to double the solar power installation capacity from 2006 to 2007.
The United States could realize an additional 69 gigawatts (GW) of solar deployment growth between 2016 and 2022 with the ITC extension.
Solar Financing
Solar system costs vary from one home and region to another. Before the system is designed, your energy consumption needs must be calculated in order to estimate the cost of such a system. Without any arrangements for financing, a large home based solar system can seem more costly than other options to an average home owner, and that will remain until technology advancement allows for substantial cost reduction.
Third party solar financing is readily available from many vendors today, but the most important news is that many offer very flexible terms. For instance, in addition to getting an initial capital to purchase and install a complete home-based solar system, you are allowed to repay the loan via monthly installments. In fact, some vendors allow you to repay the loan on a monthly basis based on the energy generated by your solar system. Depending on the vendor, it can be possible to transfer the loan to the new homeowner if you sell the home.
In addition to solar financing remember also that it is possible to claim 30% of your system’s total cost as a federal tax credit (as described above) which makes the decision to go solar even more attractive. The solar energy system can also be used as a kWh rate reduction to lower monthly charges on your bills.
Solar financing is usually undertaken under two types of contracts: leasing models and power purchase agreement (PPA).
Leasing model
A developer installs a solar power system on a client property after signing of a lease contract. The customer pays for the solar system over a given period of time – usually years. Suppose the cost of the monthly electricity bill is $150 (without the solar system) and the solar panels offset the whole energy needed. Therefore you pay nothing for electricity but you pay let’s say $100 for the solar leasing contract, which is still less than the electricity bill.
In our opinion, it’s usually better to buy the system yourself instead of leasing one, because then you enjoy the federal tax credit.
Power purchase agreement (PPA)
In this financing model, the customer and developer sign an agreement to have the solar power system installed by the developer at no cost, and the customer buys the power generated from the system. Usually, the power is sold at a fixed fee that is less than the local electricity utility charge. Both can agree that the customer purchases the system at the end of the contract period, or the contract can be extended.
Rooftop Solar Panels – Space needed, dimensions and other planning
The most common way to install a solar power system on your home is to place several solar panels on your roof. This of course means a few important planning decisions:
1) Can your roof sustain the weight of the panels?
2) Do you have enough space on your roof to place enough panels?
3) What is the best spot on your roof to place the panels in order to utilize maximum sunlight.
You can get consultation for all of the above from a professional solar installation company.
How much roof space is required?
You need to have in mind that for each 1kW of solar system you will need around 100 square feet of roof space (10’ x 10’).
For example, if you plan to install a 7kW solar panel system, you will need 700 square foot of roof space.
Common sizes of residential solar panels
Length/Width/Depth of Solar Panels
Most companies manufacture solar panels which are similar in size. For residential solar panels, the most common size is:
65 inches by 40 inches and the depth is usually 1.8 inches.
Weight of Solar panels
With standard solar panel sizes, the weight distribution of the solar panels on your roof will be around 2 pounds per square foot.
If you install a 7kW system, you will need 700 square feet space (as we’ve mentioned above) which means around 1400 pounds of distributed weight on the roof. This is not a lot and most roofs can easily support such an extra weight.
Solar Roof Shingles
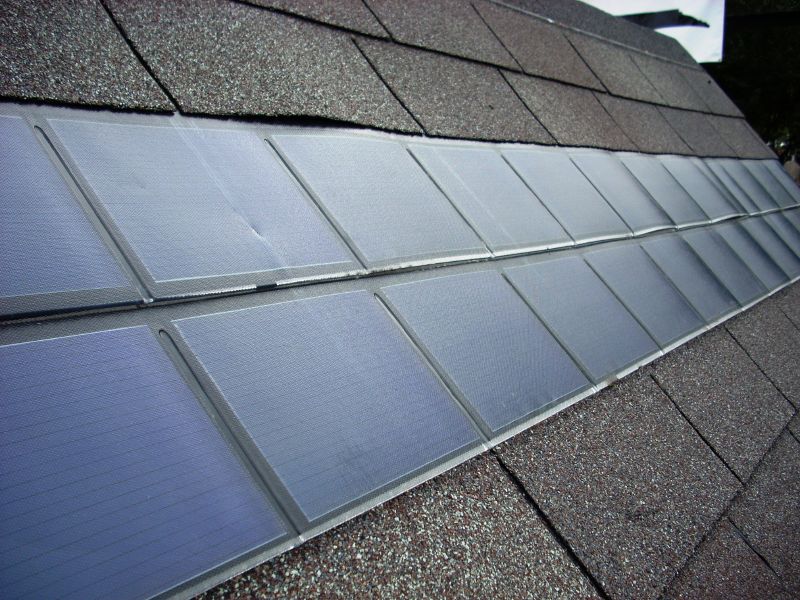

Image Source: https://www.flickr.com/photos/westbywest/1703642879/
The most common installations of solar systems use regular solar panel units. However, many home owners started looking at a new technology of solar units which have the form of roof shingles. Especially if your roof is constructed with regular roof shingles, you can replace some of them with solar roof shingles which blend in nicely with the rest of the roof (see picture above).
Each solar roof shingle acts as a regular photovoltaic cell, just as solar panels, thus producing electricity for the home.
Solar Energy Generation per USA State
The map at the following link shows solar energy generation potential of each State in the US.
http://energy.gov/maps/solar-energy-potential
As you can see, southwest states produce the most electricity.
Solar Panel Maintenance
One of the advantages of solar panels as alternative energy for your home is their low maintenance requirements (both in costs and in effort).
As a home user of the solar system, the only components that you need to take care in terms of maintenance are the solar panels (the top surface only). The other electrical components of the system (like the inverter, meter etc) do not need any maintenance and in case they malfunction you better call a professional to have a look (do not play with electricity).
The easiest and most effective way to maintain your solar panels is to clean them from dust, debris etc. You can do this using a normal garden water hose to spray water on the surface to remove dust and dirt. If it’s not possible to use a water hose, just clean them with water, soap and sponge (just like cleaning a regular window). If the solar panels are located on your roof at a spot that they are not easily accessible, it’s better to call a professional cleaning service for your panels.
The best season to clean your solar panels is during the spring so that they will have their best performance during the summer. Once or twice a year is a good maintenance frequency.
Solar Panel System Warranty
Most companies offer 25-year warranty period for the solar panel units and 10-years warranty period for the inverter.
The 25-year warranty period for the solar panels means that power output should not fall below 80% of rated power after 25 years.
Solar Panel Installation Companies
There are hundreds of solar panel installation companies in the US alone. Below we are listing the biggest ones in terms of total Megawatts installed.
Not all of the above are suitable for small residential installations though (or even the cheapest) so we advise you to get free custom quotes for your specific solar system needs.
Summary
Solar power can substitute unreliable power grids as well as help cut down carbon emissions. Besides that, it is a nice way to cut down monthly energy bills. For home uses, it is advisable to go for monocrystalline types of solar panels with highest efficiency although they are more expensive. It is also advisable to do your research for solar financing as the solar installation costs can be high in some situations without financial aid.
REFERENCES:
[1] : http://www.forbes.com/sites/ashleaebeling/2011/08/01/how-much-do-solar-panels-boost-home-sale-prices/#2715e4857a0b7328b69a29dd [2] : http://michaelbluejay.com/electricity/solar.html [3] : http://pvwatts.nrel.gov/ [4] : http://energy.gov/savings/residential-renewable-energy-tax-creditRelated Posts
- 8 Best Practices to Help Make Your Home More Sustainable
- 6 Ways You Can Cut Down Your Home’s Energy Consumption
- What are the Pros and Cons of Solar Tube Lighting in Homes
- All About Solar Panel Tiles and Shingles – Cost – Pros – Cons
- Save Your Solar Power: Maximize the Energy with These Simple Tips
- 7 Tips to Create a More Eco-Friendly Home or Apartment
Leave a Reply